Researchers at McMaster University have made an exciting discovery regarding a protein that could play a crucial role in slowing aging and preventing cellular damage. Their study sheds light on the essential process of protein homeostasis and how a newly identified protein, MANF, helps manage cellular stress, offering hope for treating age-related diseases.
Protein Homeostasis and Its Importance in Aging
Protein homeostasis refers to the body’s ability to regulate the production, folding, maintenance, and degradation of proteins within cells. Proper protein folding is vital for cell function, as improperly folded proteins can cause cellular damage and contribute to diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. When protein balance is disrupted, it leads to the accumulation of damaged proteins, which generates stress within the cell. Over time, this stress can result in cell death, contributing to neurodegenerative conditions.
MANF: A Key Protein in Managing Cellular Stress
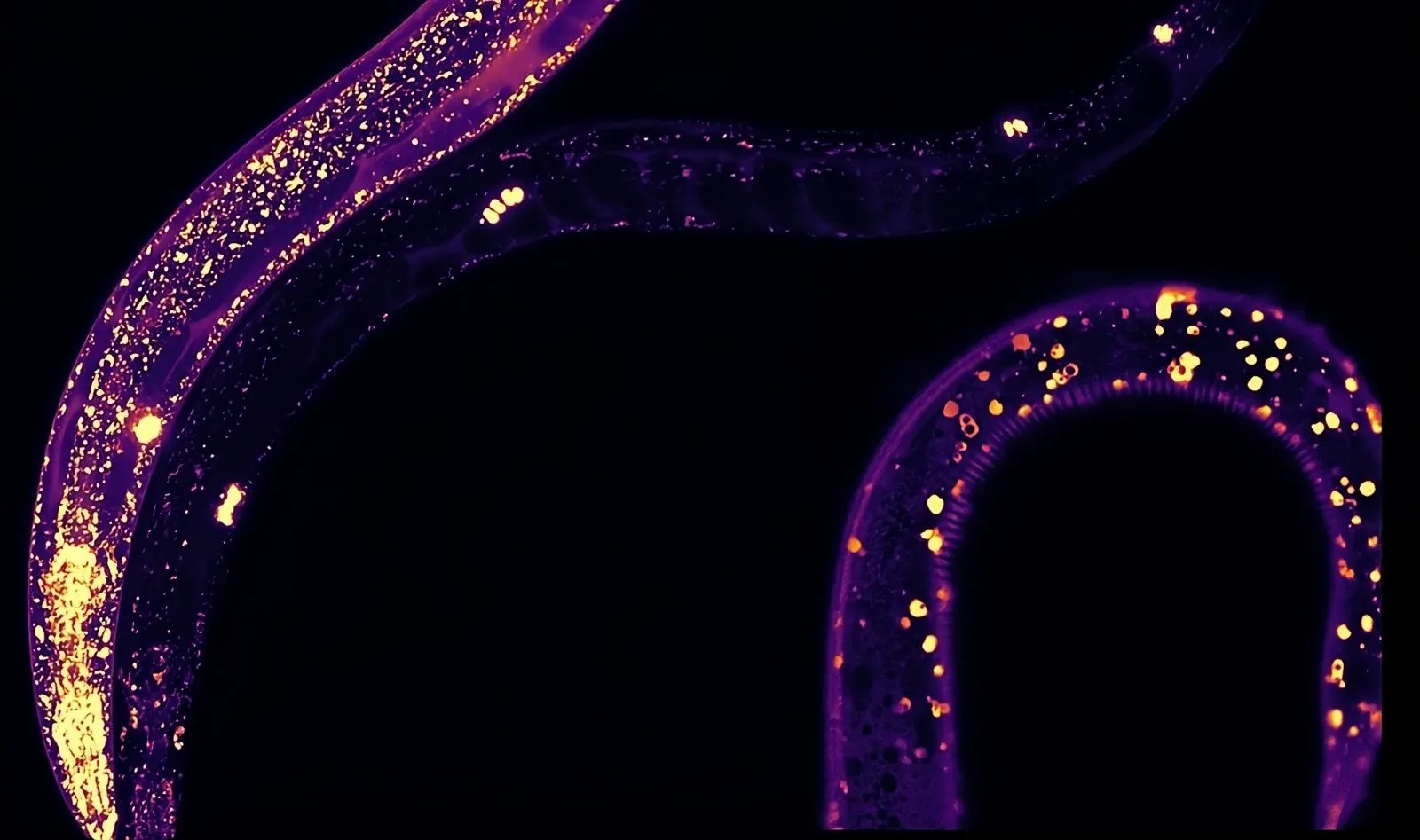
Recent research highlights the role of the protein MANF in regulating protein homeostasis. In studies using C. elegans worms, scientists discovered that MANF helps to eliminate misfolded proteins, reducing cellular stress. This process is essential for maintaining cellular balance and preventing damage that can lead to aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
The team found that increasing MANF levels in the worms enhanced their lifespan and reduced protein aggregation. This discovery opens the door for potential treatments targeting MANF to combat age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. While the study was conducted in worms, the researchers believe that the findings could be relevant to other species, including humans.
Implications for Aging and Disease Treatment
The research suggests that activating MANF’s natural protective mechanisms could be an effective way to prolong cell life and prevent the cellular damage associated with aging. By better understanding how MANF interacts with other proteins, scientists aim to develop treatments that restore protein homeostasis, offering new possibilities for addressing age-related diseases.
Though the study is still in its early stages, the initial results are promising. Researchers are continuing their investigations to apply these findings to human medicine. As they progress, this research may represent a pivotal step in the development of anti-aging therapies and treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
Conclusion
Understanding the biological mechanisms behind aging is crucial for developing effective treatments for age-related diseases. The discovery of MANF as a key player in maintaining protein homeostasis provides a new approach for combating aging and neurodegeneration. With further research, this discovery could lead to innovative therapies that improve health and longevity.