AI Unveils the Hidden Drivers of Brain Aging
As dementia diagnoses rise globally, researchers are working to identify factors that influence brain aging and resilience. At Karolinska Institutet, scientists have utilized artificial intelligence to estimate the biological age of brains from MRI scans of healthy seniors. Their findings highlight how health conditions like inflammation and diabetes accelerate brain aging, while lifestyle factors, such as regular exercise, appear to slow it down. These results were recently published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
How AI Estimates Brain Age
Every year in Sweden, over 20,000 people are diagnosed with dementia, two-thirds of which are Alzheimer’s cases. To explore ways to mitigate brain aging, researchers turned to artificial intelligence.
“Even with new Alzheimer’s drugs, they won’t work for everyone, so understanding how to enhance brain resilience remains critical,” explains Anna Marseglia, lead author and researcher at Karolinska Institutet.
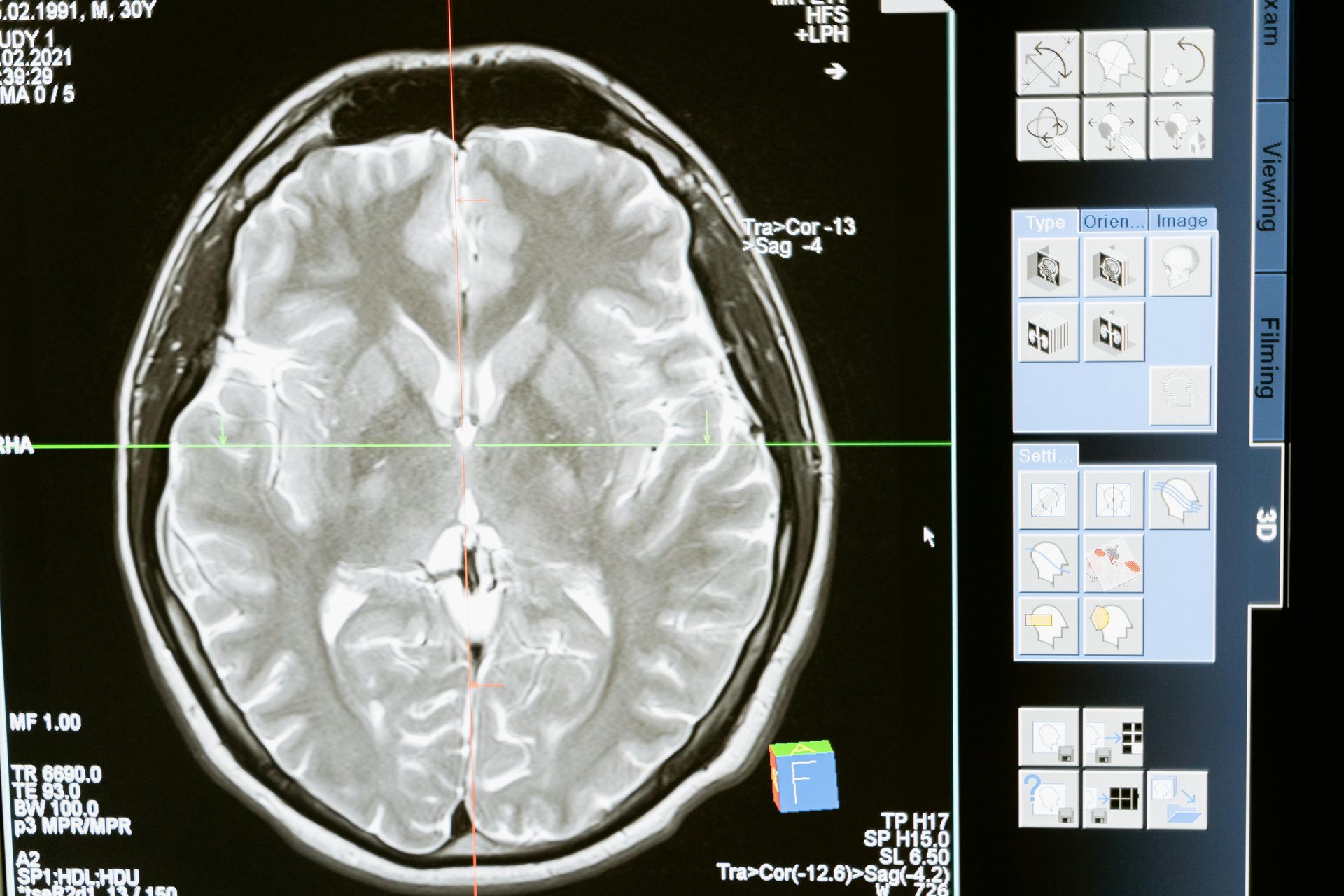
The study involved 739 cognitively healthy 70-year-olds, with 389 women participating, all part of the Gothenburg H70 cohort. Using AI-driven algorithms, the researchers estimated each participant’s brain age from MRI scans.
“The tool is both precise and user-friendly,” says Eric Westman, principal investigator and neurogeriatrics professor. “Although it requires further validation, we envision its future use in clinical settings, such as during dementia evaluations.”
Blood samples were analyzed for glucose, lipids, and inflammatory markers, while lifestyle factors, cognitive test results, and medical histories were also assessed.
Key Factors Influencing Brain Health
On average, the AI estimated the biological brain age to be 71 years, nearly matching participants’ chronological ages. By calculating the “brain age gap” (the difference between biological and chronological brain age), the researchers identified key health and lifestyle influences.
Conditions such as diabetes, strokes, and small vessel disease correlated with older-appearing brains. Conversely, maintaining vascular health through regular exercise and stable blood glucose levels was linked to younger-looking brains.
“Keeping your blood vessels healthy is crucial for protecting your brain,” Marseglia emphasizes. “Stable blood glucose levels, for instance, play a significant role in maintaining brain health.”
Next Steps in Brain Resilience Research
Interestingly, the study found differences in how men and women build resilience to brain aging, suggesting a need for further gender-focused research.
“Next year, we plan to examine how social engagement, support, stress, and sleep influence brain resilience, with a particular focus on women,” says Marseglia. Researchers aim to understand the interplay between sociocultural factors and biological determinants, such as hormonal changes, in aging brains.
Brain Aging: Future Implications for Healthy Aging
The study represents a significant step in uncovering how lifestyle and health choices influence brain aging. By identifying modifiable risk factors and protective behaviors, this research opens doors to developing strategies that enhance cognitive health and resilience.