Agibot Breaks Ground in Humanoid Robotics
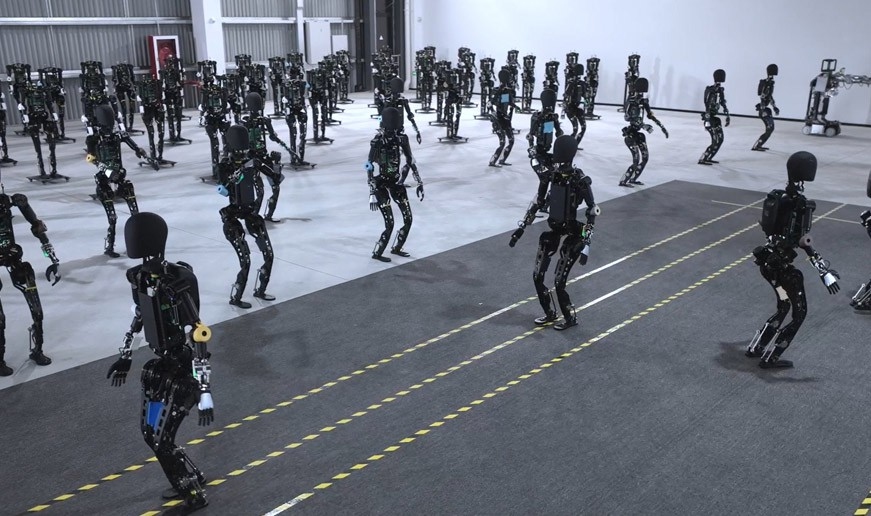
Agibot, a Chinese robotics company launched in February 2023, has taken the tech world by storm with its groundbreaking achievement in humanoid robot production. By the end of 2023, the company, also known as Zhiyuan Robotics, announced it had produced nearly 1,000 general-purpose robots, marking a milestone in the industry.
Meanwhile, Tesla, the American electric vehicle giant, has set its sights on high-volume humanoid robot production by 2026. Elon Musk hinted earlier this year that Tesla’s robots will be available for internal use in 2024, with broader commercial applications expected thereafter. However, Agibot’s early success has positioned it as a direct competitor to Tesla’s Optimus robot.
A Factory Fueled by Innovation
Agibot shared a video showcasing its advanced manufacturing facility in Shanghai’s Lingang Fengxian district. The factory’s production line integrates human workers and self-manufactured humanoid robots, collaborating on tasks such as inventory shelving and component testing.
Additionally, the company has established a “data collection factory” to enhance real-world AI capabilities. Robots undergo training in various household tasks, including folding clothes, organizing spaces, cleaning, and laundry. These efforts demonstrate Agibot’s focus on practical applications and real-world functionality.
Global Robotics Race: China vs. the US
Although Tesla and other US tech companies dominate in high-end chip production, precise manipulation, and cloud computing, Chinese firms like Agibot excel in motion control, AI model development, and low-cost manufacturing. According to industry experts, China’s well-established supply chain gives it a competitive edge in scaling humanoid robot production.
Wei Jiaxing, an expert from the National and Local Co-built Embodied AI Robotics Innovation Center, emphasized China’s commitment to independent research and specialized robotics chips. He noted that while challenges like efficiency and stability persist, China’s manufacturing prowess makes it better positioned for high-output robot production at lower costs.
Expanding Applications and Market Potential
The industry is now shifting its focus toward practical applications for humanoid robots. Agibot and other Chinese firms, like Fourier Intelligence and UBTech Robotics, are exploring scenarios in healthcare, logistics, and domestic assistance to ensure broader market adoption.
Despite the excitement, industry insiders caution that mass production will depend on customer demand and the readiness of scenarios for large-scale deployment. “The key is achieving maturity and reliability in technology and products,” said Wei. Only then will companies be able to fully capitalize on their production capacities.
China’s robotics industry is poised for rapid expansion, but hurdles such as technical inefficiencies and global competition remain. As 2024 approaches, companies like Agibot are reshaping the landscape of humanoid robotics, setting the stage for a new era of intelligent machines.